Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Life
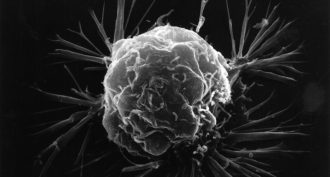
LifeCell gangs may help cancer spread
A new study on mice suggests that when cancer cells strike out from a primary (first) tumor in groups, they have an especially good chance of creating new tumors elsewhere.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureLivestock: A need to save rare breeds
New studies and ongoing work highlight why society should save rare livestock breeds — and the part that technology can play.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhy animals often ‘stand in’ for people
Rats, birds, fish — even flies and worms — can stand in for people in laboratory testing. This allows scientists to safely evaluate harmful chemicals as well as to identify and test potential new drugs. But such tests will never be a foolproof gauge of effects in people.
-
 Microbes
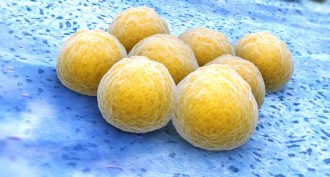
MicrobesGerms help each other fend off antibiotics
Drug-resistant bacteria can cause persistent infections. A new study finds these germs fight drugs in different ways. And they can swap various compounds, increasing their neighbors’ chances of overcoming the drugs meant to kill them.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHigh-altitude help from extinct ancestors
The Tibetan plateau is high in altitude but low in oxygen. An unusual version of one gene in Tibetans' DNA helps them survive this environment. And that gene appears to have been passed along from Denisovans, a Neandertal-like ancestor.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNewfound DNA ‘enhancer’ behind many natural blonds
Some snippets of DNA other than genes play a role in giving some people of European a golden crown of hair.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen a species can’t stand the heat
When temperatures rise, New Zealand’s tuatara produce more males. With global warming, that could leave the ancient reptile species with too few females to avoid going extinct.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeen uncovers new weapons to stop Huntington’s disease
David Seong, an Intel Science Talent Search finalist, is studying how tiny pieces of genetic material might be used to lock up a dangerous protein in Huntington’s disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple test for cancer and heart disease
Disease diagnosis often requires expensive equipment and tests to probe deep inside the body. But a new test relies on a fast, cheap and easy technique. And its answers appear on a strip of paper — just as they do on a pregnancy test.
-
 Brain
BrainWhy boys face higher autism risk
Boys develop autism at four times the rate seen in girls. Girls’ genes are better protected from the mutations linked to this brain disorder, data now suggest.
-
 Life
LifeCaught in the act
Scientists observe some evolutionary speed demons as they adapt over the course of just a few years to new environmental conditions.
-
 Animals
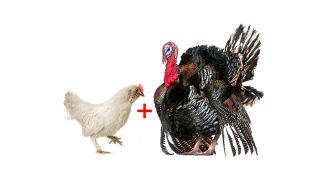
AnimalsChurk: Not for Thanksgiving
Here’s what happens when livestock breeders cross a chicken and a turkey
By Janet Raloff