MS-ESS1-4
Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth's 4.6-billion-year-old history.
-
 Earth
EarthA rainforest once grew near the South Pole
A forest flourished within 1,000 kilometers of the South Pole. That was a while ago, as in millions of years ago.
-
 Space
SpaceBlack hole mega-burp was truly explosive
Long, long ago, in a galaxy far, far away, a black hole blasted out 100 billion times as much energy as our sun ever will. One word for that: Wow!
-
 Earth
EarthStudy appears to rule out volcanic burps as causing dino die-offs
New data on when massive volcanic eruptions happened do not match when the dinosaur mass extinction took place.
-
 Space
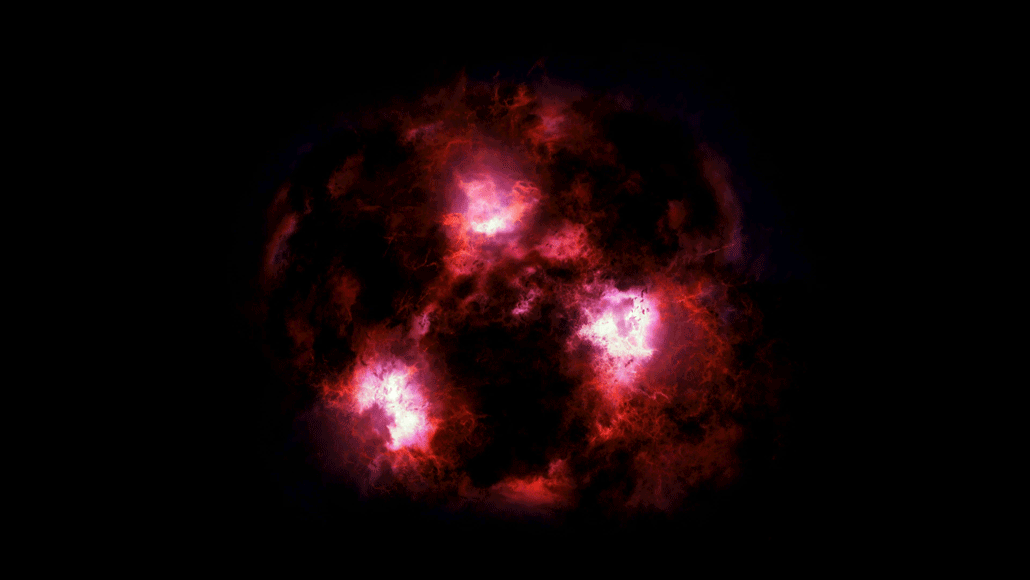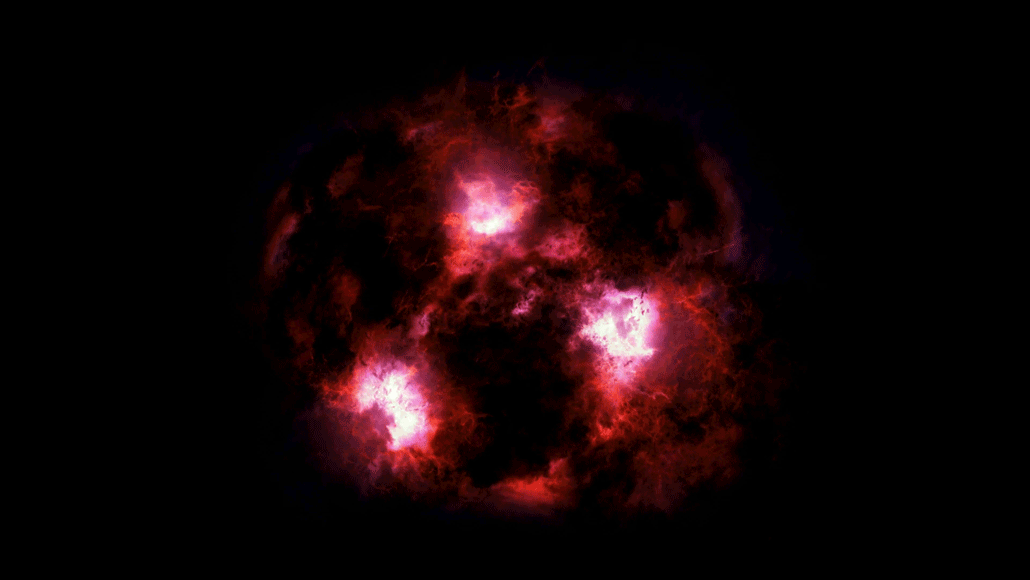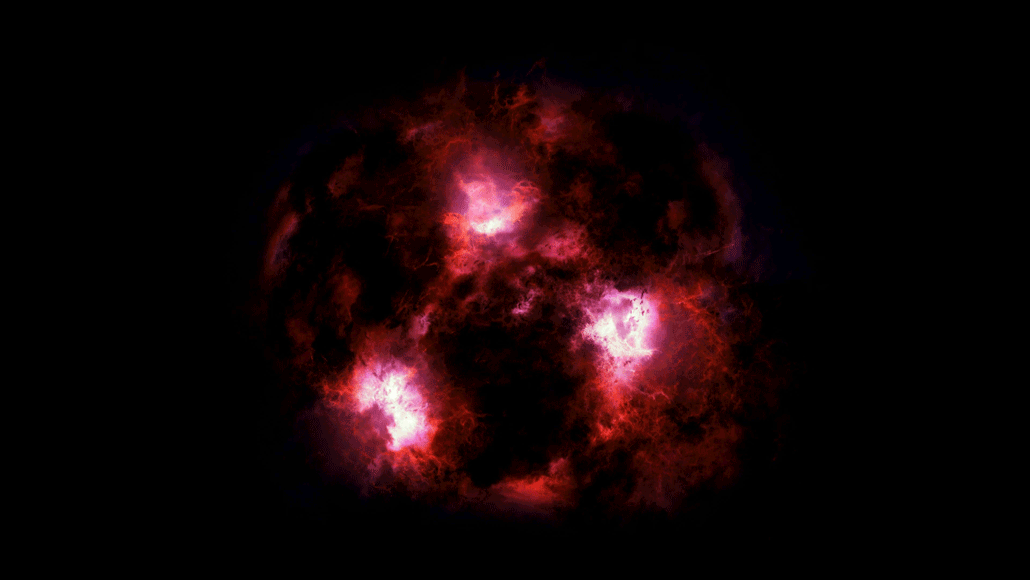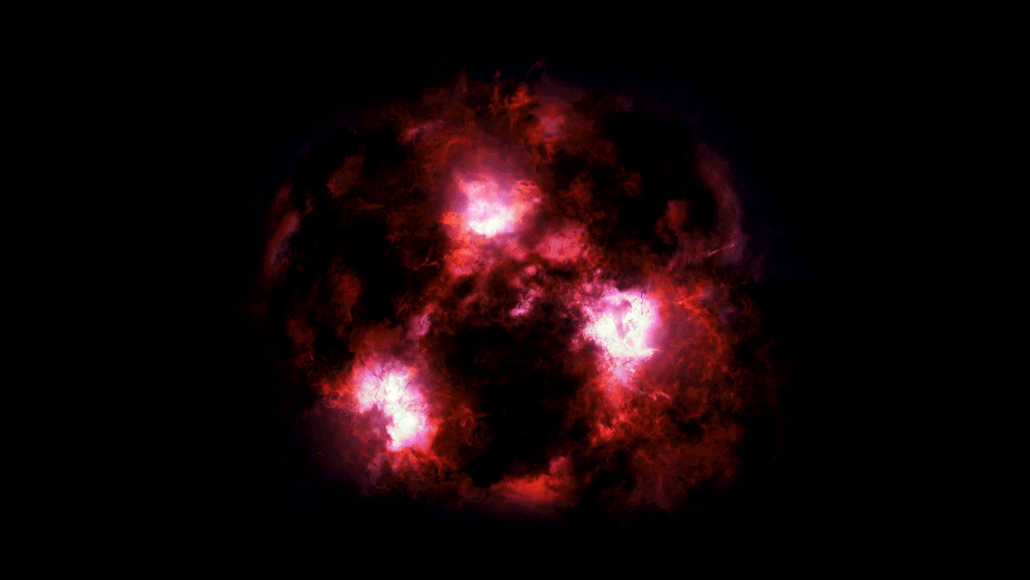
SpaceDust-shrouded monster is a snapshot from the early universe
Scientists have spotted a massive galaxy from the early universe shrouded in dust. It turned up in a small survey by the ALMA radio telescopes in Chile.
-
 Planets
PlanetsHow Earth got its moon
How did our moon form? Scientists are still debating the answer. It may be the result of some one big impact with Earth — or perhaps many small ones.
-
 Earth
EarthIs Zealandia a continent?
Geologists are making the case for a new continent, that they would dub Zealandia. It can be found largely submerged beneath the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
-
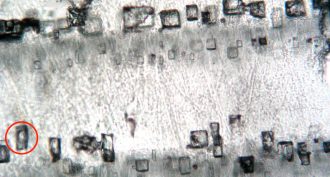 Earth
EarthOxygen-rich air emerged super early, new data show
Scientists had thought animals were slow to emerge because they would have needed oxygen-rich air to breathe. A new study finds that plentiful oxygen may have developed early. So animals may have been late on the scene for another reason.
-
 Earth
EarthCool Jobs: Mapping the unknown
Scientists find different ways of exploring places humans will never visit — and drawing maps to help us better understand such mysterious places.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Space
SpacePollution may give ‘first’ stars a youthful look
The oldest stars should be made of only light elements. But these suns may have sucked up heavier elements, giving them a more youthful appearance, a new study finds.
-
 Planets
PlanetsAsteroids boiled young Earth’s oceans
At least two asteroids hit Earth 3.3 billion years ago. This superheated the atmosphere, boiled the oceans and shaped how early life evolved.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCooking up life for the first time
The basic components for life could have emerged together nearly 4 billion years ago on the surface of Earth, chemists report.
By Beth Mole -
 Space
SpaceAstronomers spy fastest speeding star
A few stars have been spotted departing our galaxy. The fastest of these might have been propelled by another exploding star, a new study finds.