MS-LS2-4
Construct an argument supported by empirical evidence that changes to physical or biological components of an ecosystem affect populations.
-
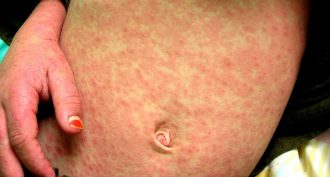 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine10 things to know about measles
Many people think that the measles vaccine wiped out the disease — at least in the United States. It hasn’t. And people who were never vaccinated face the primary risk of getting this very serious disease
-
 Animals
AnimalsHellbenders need help!
Hellbenders already face threats such as habitat loss, pollution and disease. But climate change could make matters worse. And the problems facing hellbenders could spell trouble for more than just these giant amphibians.
-
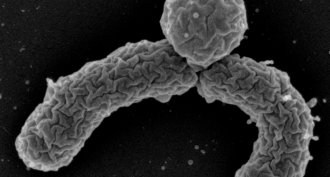 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew germ fighter turns up in dirt
Scientists have found a compound in soil that can kill the microbes that cause anthrax, tuberculosis and other diseases.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesOngoing Ebola outbreak traced to hollow tree
Scientists suspect the current Ebola outbreak started with bats that lived in a hollow tree in Guinea. The outbreak's first victim, a two-year-old boy, often played in the tree.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists say: Biomagnify
Chemicals in the environment can build up in an animal’s tissues. Predators who feed on these animals can accumulate more and more of the pollutants, a process known as biomagnification.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPicture This: Winter brings white noses
White-nose syndrome, caused by a fungus, has killed millions of bats in the eastern United States. Now, scientists show that the disease comes and goes, by season. The finding could help scientists more effectively target any treatments.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentSpidey sense: Eight-legged pollution monitors
Spiders that prey on aquatic insects can serve as sentinels that naturally monitor banned chemicals that still pollute many rivers across the United States.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesHow ‘bugs’ in our bellies impact our health
Gut bacteria can play a powerful role in human health, new studies show. In one, bacteria turned a nutrient in red meat into a chemical that boosts the risk of a heart attack. Another study shows that our genes play a role in whether we are fat or thin, probably by affecting which bacteria prefer to live in our intestines.
-

Food can make an appetizing science fair project
Many students think they need a laboratory or special equipment for a winning research project. But finalists at the Broadcom MASTERS competition showed food-based research may require little more than your home kitchen
-
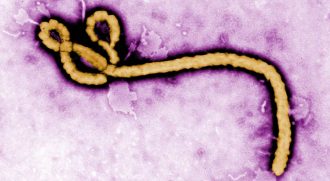 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is Ebola?
A virus is behind the hemorrhage-inducing infection called Ebola. It causes fevers and often intense bleeding — seemingly from anywhere and everywhere.
By Janet Raloff -
 Environment
EnvironmentBug-killer linked to decline in birds
One of the most popular chemicals used to protect crops from bugs may also take a toll on birds, a Dutch study finds. U.S. farmers also rely on these insecticides, a second study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTeen shows salty lionfish are getting fresh
Lauren Arrington kept spotting lionfish in rivers near her Florida home. Her science fair project probed how much fresh water these ocean fish could stand — and led to a published research paper.