Humans

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Health & Medicine
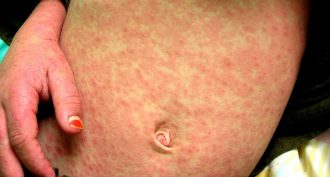
Health & Medicine10 things to know about measles
Many people think that the measles vaccine wiped out the disease — at least in the United States. It hasn’t. And people who were never vaccinated face the primary risk of getting this very serious disease
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMost students wrong on risks of smoking occasionally
Teens know that heavy smoking can seriously harm health. But most, a new study finds, don’t realize that smoking only now and then also is harmful. Data from a survey highlight teens’ mistaken ideas about the risks of intermittent smoking.
-
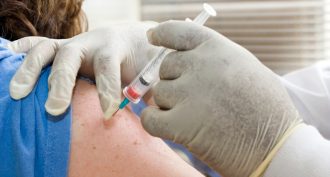 Environment
EnvironmentImmunity: Environment can have big impact
A study on twins suggests that environmental factors can shape a person's immune system more than genes do.
-
 Brain
BrainA new ‘spin’ on concussions
Scientists have suspected that rotational forces in the brain may underlie concussions. A new study used athletic mouthguards containing sensors. Data on head movements during collisions suggest that a twisting of the brain may underlie mild brain injuries, including concussion.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesOngoing Ebola outbreak traced to hollow tree
Scientists suspect the current Ebola outbreak started with bats that lived in a hollow tree in Guinea. The outbreak's first victim, a two-year-old boy, often played in the tree.
-
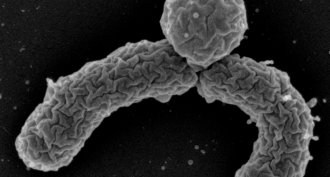 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew germ fighter turns up in dirt
Scientists have found a compound in soil that can kill the microbes that cause anthrax, tuberculosis and other diseases.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAir pollution can mess with our DNA
New research suggests a type of air pollution — diesel fumes — can affect your health. It inappropriately switches some genes on, while turning off others.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA whale of a lifespan
Bowhead whales can live more than 200 years. The secret to such longevity may lie in the Arctic species’ genes. Scientists recently mapped the whale’s genetic code. They found features that protect the marine mammal against cancer and other problems related to old age.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesCold noses nurture colds
The common cold infects the nose. Scientists long have known the virus grows better there, but not why. Now, a study finds the body’s defenses simply don’t work as well under the nose’s slightly cooler temperatures.
-
 Computing
ComputingVirtual wounds: Computers probe healing
To better understand how the body heals wounds, scientists have begun creating computer programs that let virtual cells fight it out. These ‘computer games’ could lead to better medicines.
-
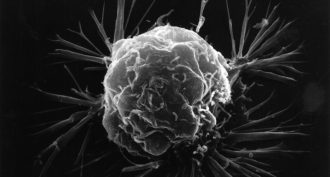 Life
LifeCell gangs may help cancer spread
A new study on mice suggests that when cancer cells strike out from a primary (first) tumor in groups, they have an especially good chance of creating new tumors elsewhere.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists say: Inflammation
When cells are injured, they send out distress signals. The rescuing cells cause more blood to flow to the area, producing inflammation.