
Tech
Gravity ‘batteries’ might help a weighty renewable-energy problem
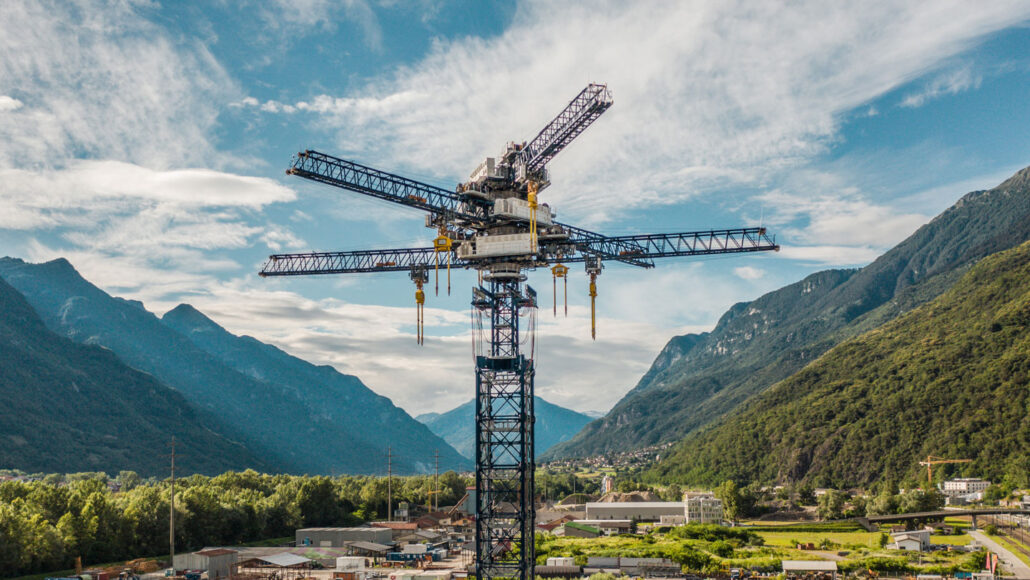
To store the energy generated by wind and solar power, researchers are looking at mammoth systems that raise and lower weights.
Come explore with us!

To store the energy generated by wind and solar power, researchers are looking at mammoth systems that raise and lower weights.

This property causes materials — including some animals’ skin, fur or feathers — to glow under light.

These hydrogel “jelly ice cubes” are made mostly of gelatin and water. They won’t melt, even when thawed, and may provide new food cooling options.
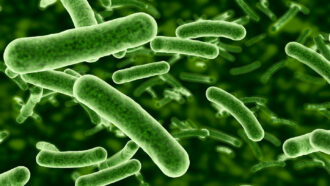
A new study shows how some microbes absorb and release electrons — a trait that may point to new fuels or ways to store energy.

An electrode’s name depends on the circumstances. Confused? It may help to consider which electrochemical reaction is natural — and which is not.

A fluorescent polymer duo boosts the efficiency of solar cells. One day this material may coat your jacket, hat or backpack to provide power on the go.

Baking soda volcanoes are a fun demonstration, and with a few tweaks they can be an experiment, too

New measurements of a weird but simple atom, one without a nucleus, suggest it may have unexpected properties. Scientists find this troubling.

Here’s how to freeze a soap bubble in midair. Warning: The environment needs to be frosty, and even then it can take a certain amount of trial and error.

A special coating that conceals temperature information from heat-detecting cameras might someday be used as a privacy shield.