Earth

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Fossils
FossilsDino double whammy
Most scientists think an asteroid helped kill off the dinosaurs. But new calculations suggest that asteroid might have gotten some help from a long series of volcanic eruptions in what is now India.
-
 Climate
ClimateThunderstorms can generate powerful radiation
Thunderstorms don’t just hurl lightning bolts. Some churn out high-energy radiation that can be seen by spacecraft. This radiation offers scientists a glimpse of the inner workings of thunderclouds.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesClouds may be dining cars for some germs
Scientists had known microbes could hitchhike across and between continents on clouds. New research now shows that some germs don’t just treat clouds as a high flying jet, but also as a cafeteria.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
EnvironmentSpidey sense: Eight-legged pollution monitors
Spiders that prey on aquatic insects can serve as sentinels that naturally monitor banned chemicals that still pollute many rivers across the United States.
By Beth Mole -
 Environment
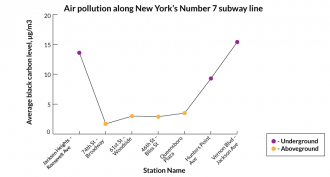
EnvironmentSoot fouls subway stations — and maybe lungs
Soot levels in stations for New York City’s electric subway trains exceed the levels outdoors, a new study finds. The underground source of this black carbon: maintenance trains that share the tracks with subway trains. Breathing soot can aggravate asthma and other lung disease.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Environment
EnvironmentNano air pollutants strike a blow to the brain
Most people think that air pollution poses the biggest risk to our lungs. In fact, pollution hits the brain too, sometimes by traveling a direct route — through our noses. These tiny pollutants can harm IQ and more.
-
 Fossils
FossilsTar pit clues provide ice age news
New analyses of insects and mammals trapped in the La Brea Tar Pits point to climate surprises during the last ice age.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change brings new neighborhood birds
Climate change has made winters a little bit warmer. Many bird species are now wintering a lot farther north than they did a few decades ago, a new study finds.
-
 Earth
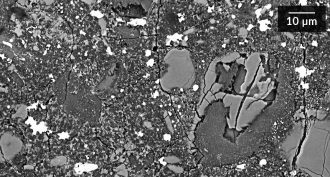
EarthEarth’s most common mineral finally gets a name
A half-century search for samples of Earth’s most abundant mineral has ended. This stuff forms only deep in the rocky layer surrounding our planet’s core. But scientists found bits of it in a meteorite that fell in 1879. And finally, this bridgmanite gets a name.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentADHD linked to air pollutants
Air pollution from cars and industries can spew pollutants known as PAHs. A new study shows children have a greater risk of ADHD if their mothers inhaled a lot of PAHs while pregnant.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentThirdhand smoke poses lingering danger
The pollutants in cigarette smoke can linger indoors for hours. Indeed, they may pose risks long after any visible smoke is gone.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateThe worst drought in 1,000 years
The 1934 drought, during a period in American history known as the Dust Bowl, was the worst in a millennium, a new study finds. While the drought had natural origins, human activities made it worse.
By Beth Geiger