Materials Science
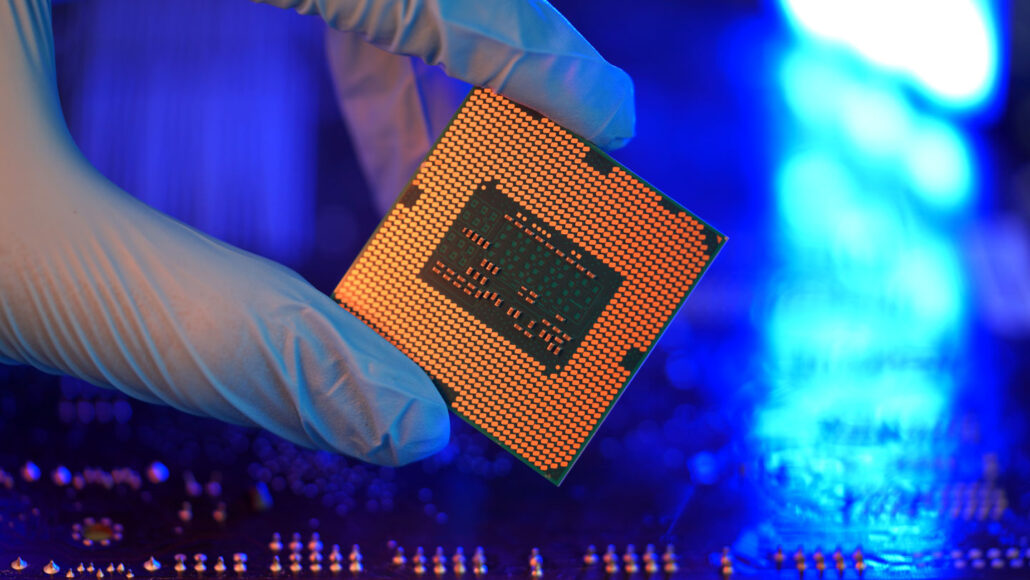
Scientists Say: Semiconductor
Modern electronics, from cell phones to video games, work thanks to these conductor-insulator hybrids.
Come explore with us!

Modern electronics, from cell phones to video games, work thanks to these conductor-insulator hybrids.

Scientists have been trying to understand and harness this material’s superpowers since its discovery in 2004.

Researchers in Sweden coaxed wood to conduct electricity, then used it to make a climate-friendlier building block of electronics.

Scientists made a device that converts the greenhouse gas into formate. This salt can then run a fuel cell to make electricity.
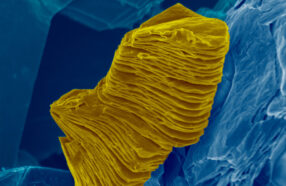
To slow global warming, we’ll need help from CO2-trapping materials. Enter MXenes. They’re strong and reactive — and they love to eat up CO2.

A new coating made from a renewable resource — water-loving nanoparticles made from wood — could keep glass surfaces fog-free.

The salty gel absorbs more water from the air than similar gels, even in desert climates. This could provide clean water for drinking or farming.

The award honors three scientists who discovered and built quantum dots, which are now used in everything from TVs to medical tools.

Rare earth elements aren’t all that rare — but skyrocketing demand for these metals makes them precious.

If made under gentle conditions, leather formed from the “roots” of mushrooms can retain the ability to regrow and repair minor damage.